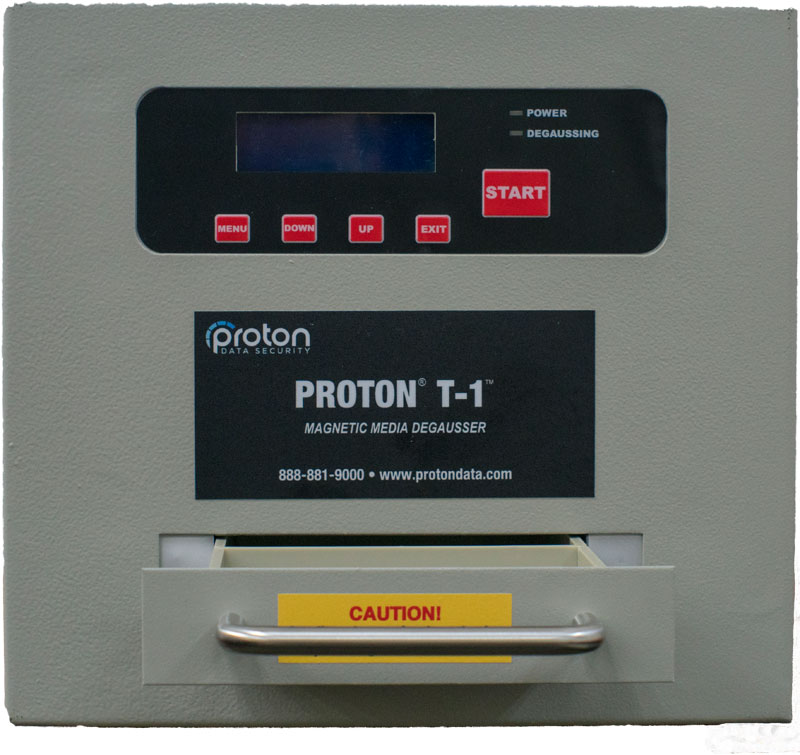
DEGAUSSER:
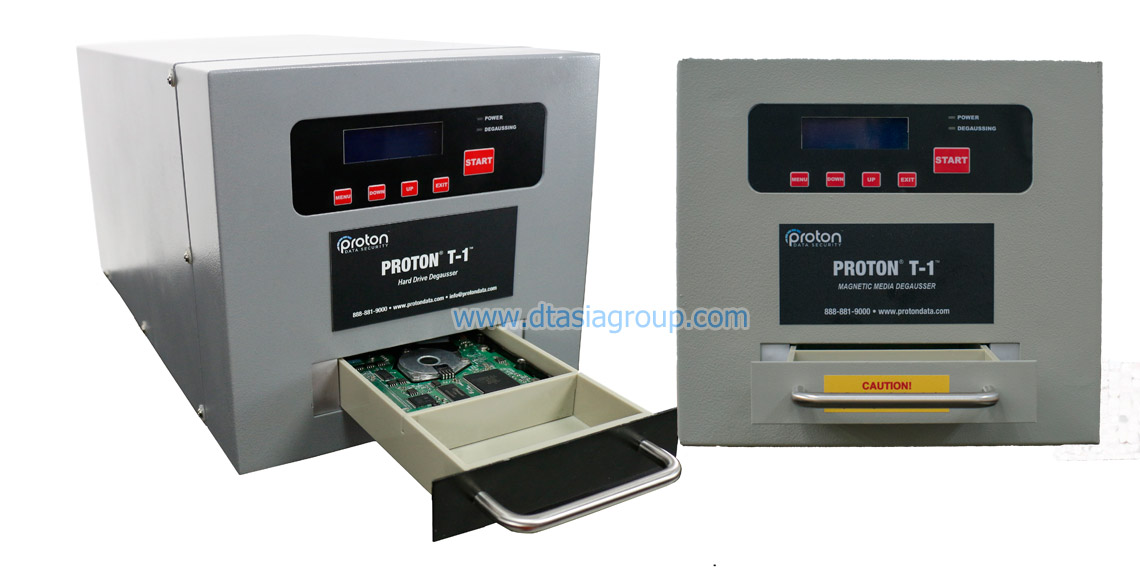
Degausser is a machine used to eliminate data stored on computer and laptop hard drives, floppy disks and magnetic tape, by randomly changing the alignment of magnetic domains on the medium.
Data is stored on magnetic media by making very small areas called magnetic domains change their magnetic alignment to be in the direction of an applied magnetic field. Degaussing magnetic media leaves the domains in random patterns with no preference to orientation, thereby rendering previous data unrecoverable. A degausser is therefore used to completely erase all audio, video and data signals from magnetic storage media.
This process is effective in a range of industries including video, audio, computer, broadcast and data security.

Benefits of Using a Degausser
- Assurance that all sensitive data has been erased permanently
- Disposes classified media quickly, safely and in-house
- Improvement in the quality of output
- Sizeable savings in operating costs
- Meets the NSA and CESG requirements for sanitisation of classified information
Simply overwriting magnetic media does not completely erase data. Only a degausser can remove data 100% and ensure that confidential data is securely and completely erased.
How does a Degausser work?
It works by passing any magnetic media through a powerful magnet field to rearrange the polarity of the particles, thus completely removing any resemblance of previously recorded data. Although this process of course is simple in theory, in practice, the vast variation of media formats and magnetic densities makes the correct process quite difficult to achieve. The degausser is constructed in such a way as to enable the generated magnetic field to be available to the media when it is transported through it, which can be by physically holding the media and moving it through the field by hand, having it automatically conveyed by a belt transporter or rotated on a motorized spindle.
Different media demand varying magnetic field strength, therefore the coils that generate the magnetic field will also vary depending on this requirement. Generally speaking, a coil is a degausser which should have two to three times the energy rating of the material being degaussed. Where media has a security classification, Restricted, Confidential, Secret or Top Secret, a considerably higher energy rating will be required. This rating is measured in Oersteds. Further efficiency can be achieved by using more than one coil in multi-axial orientation; this produces a more effective degaussing field. Even better performance can be achieved by rotating the coils or the media during the process.
Operation of Degaussers
The operation of degaussers will vary depending on the type and quality of media and the speed and degree of erasure required. When erasing tapes, either the cassette must move through the magnetic field or you must move a magnetic field over the cassette. In each case, the consistency of the motion, the strength of the field and the distribution of that field over the entire media are what determine the quality of the erasure.
Most professionals and engineers agree that a conveyor transport degausser, which allows the user to place the magnetic media on a small belt, which in turn passes the media through or over the degaussing coils at a constant speed, assures the most uniform process. Custom-designed degaussers can assist with the specialist needs of bulk operators with belt feed conveyors; collection hoppers are available to deal with tapes, disks and reels, all helping in making the operation effective & efficient.
Effective degaussing is very much a performance factor of the machine and generally passing the media through the field twice does not improve the effectiveness. However, if the media is rotated by 90 degrees, some improvement can be achieved. VS Security Products have developed an eraser employing “state of the art” technology that uses a rotating coil technique. The media passes on a variable speed conveyor belt through a field, generated by two powerful coils, which are rotating, one above the media, the other beneath it.
With the ever-increasing demand to fit more & more data on smaller media, there is now a requirement that can be more important than absolute erasure. That is consistency of erasure.
It is widely understood that data at a high packing density stored on magnetic media is easier to erase than lower density data. The data signal to noise ratios, bit-to-bit phase relationships, amplitude variations all become more critical and require more sophisticated electronics to ensure valid error free data recovery. Variations of magnetic flux, remaining from a poor erasure cycle, will make data recovery more difficult and will result in increasing errors.
Detailed Benefits of Degaussers
The resultant benefits are substantial, producers of audio and video tapes achieve better yields as well as increased quality. Data users enjoy greater efficiency due to considerably reduced “error rates”. Professional users in every sector, from government to business, benefit from incorporating degaussing within their magnetic media processing procedure and achieve considerable cost savings by being able to confidently reuse again and again media previously discarded.
The controlled application of degaussers to the process involved in the production & operation of magnetic media can achieve considerable savings. For a start, many operators who do not currently degauss, simply throw away suspect media that, with a careful process of degaussing applied to it, would have a considerable extended life. Many operators claim benefit of up to four times the useful life of some types of media.
Further direct & indirect savings can also be achieved. Quality of performance of the media has a very high value, although it would be difficult to qualify. Indirectly, there are additional cost savings to producers and to end users due to the considerable reduction of “down time” of computers and data processing apparatus arising from faulty or imperfect magnetic media being used. Diskette duplicators claim to gain upwards of 25% better production yields directly attributable to degaussing their bulk bland diskettes, prior to processing.
Another benefit is that magnetic media is very difficult to dispose of. If it is burned, it emits toxic fumes, if it is buried, it is not biodegradable. By re-using your media as many times as possible, you are adding you your company’s recycling program.
The amount of magnetic media used in the broadcast, computer and software industries has resulted in professional users striving to achieve higher quality and efficiency, whilst at the same time searching for cost savings. By degaussing magnetic media using “deep erasure”, created by powerful magnetic fields, users or producers find that previously recorded data, or certification signal can be eliminated completely from tapes, cassettes or cartridges. The effectiveness that this method of erasure achieves far exceeds that of DC erasure (this is the method that is used in hard disk drives).
Who uses a Degausser?
Anybody who uses magnetic media will benefit from the use of a degausser, including:
- Radio/Television broadcasters: enables expensive tapes to be re-used
- Computer departments of corporations: allows re-use of back up tapes and safe disposal of information from PC hard drives
- Data Storage Companies: data no longer needed can be easily and efficiently erased
- Defense Organizations: confidential and top secret information can be erased
- CCTV Operators: allows VHS tapes to be re-used again and again
- Audio/Video duplicators: allows re-use of any production over runs and returned out of date tapes
- Financial Services: Banks and insurance companies can use a degausser to re-use magnetic media for voice logging systems
- Emergency Services: Re-use tapes used in voice logging systems
- Hospitals: erase sensitive information held on magnetic media, such as patient records no longer required
- Universities: allows student records that are no longer needed to be erased
Problems in a Degausser
A coil degausser employs a steel core wrapped in copper wire that creates an alternating electromagnetic field when activated. This magnetic field is always present when the degausser is powered up, which can overheat the coil. A disadvantage of this type of degausser technology is that it creates very high levels of heat, so these degaussers oftentimes have a short operational cycle, ranging anywhere from one minute to several minutes before requiring a longer cool-down period before they can be reused. The AC degausser must have a limited duty cycle to protect the coil from overheating. Larger coil degaussing machines utilize fans to keep the coil as cool as possible and extend the operating cycle. Many hand-held degausser units as well as manual and conveyor machines employ the use of a coil.
The Conveyor Belt Degausser
The Conveyor Belt Degausser works with an electromagnet underneath a conveyor belt. The devices are hovered over the electromagnet and the magnetic field will be destroyed and with it all of the data.
Problem: This procedure has to be done several times since it is not certain that all of the sectors of the device were targeted and the data was securely deleted. Additionally the hard disks have to be switched from top to bottom in this process, either manually or by the machine.
The AC-Degausser
The AC-Degausser looks like a scanner device with a glass surface, where the hardware – either a hard disk or a tape – will be placed on. As with the Conveyor Belt Degausser one strong electromagnet is directly placed underneath the middle of the glass plate. When degaussing, the user has to lay the disk or the tape directly over the glass and turn it several times.
Problem: There are several pitfalls to this technology. It is a totally manual operation which has to be done several times since one cannot be certain that the whole device is totally freed from data in one pass. Additionally, it is advised that the user should wear protective hand gloves since he gets in near contact with the magnetic field while he is turning the disks or tapes over the glass. For some time now doctors and researchers have warned about the risk of getting cancer if one is excessively exposed to magnetic fields.
The Permanent-Magnet-Degausser
This Hardware works with two rare natural magnets with high field strengths. The medium which is to be erased will be moved between the two magnets thus deleting all data. The magnets are “always on”.
Problem: Since the magnets are always active, the hardware has to be secure from allowing magnetic fields to ‘leak’ out of the hardware and to the user. To protect against this most of these devices are quite big and therefore are only useable in one specific place.
The Impulse-Degausser
The Impulse-Degausser uses an electro-magnetic coil. Once started, it sends a high frequency electro-magnetic impulse – via built-in and fully loaded capacitors – through the coil, which destroys all data on the disk or tape. The medium to be erased is put inside the coil to cover all of the plates with the magnetic field. With this technology hardware degaussers can be built relatively small, easy to transport and are less energy consuming than the other technologies used.
The “mixed” Impulse/Permanent Magnet Degausser
This Technology uses both permanent built-in magnets to delete data and additionally sends an impulse through a coil to “finalize” the process.
Problem: Even though the idea is great it gives no additional benefit to the customer beyond a single degaussing solution. Also, the cost is normally higher than a device with just one technology built in.
 What happens to all the personal documents, pictures, private emails, programs, passwords, credit card details, etc that are on it?
What happens to all the personal documents, pictures, private emails, programs, passwords, credit card details, etc that are on it?